Learn the key differences between diminished value and depreciation, why they matter for car owners, and how they impact your vehicle’s worth. Get the full breakdown here.
What Is Diminished Value?
Diminished value is the reduction in your car’s market value after it has been damaged and repaired, even if the repairs are done perfectly. This concept is particularly relevant after accidents, as potential buyers may perceive the vehicle as less valuable due to its history.
Definition of Diminished Value
Diminished value is the difference between your car’s pre-accident value and its post-repair value. For example, if your car was worth 20,000 before an accident and only 17,000 after repairs, the diminished value would be $3,000.

How Diminished Value Occurs
Diminished value occurs because of the stigma associated with accident-damaged vehicles. Even if repairs are done correctly, buyers may worry about hidden damage or future issues, leading them to offer less for the car.
H3: Types of Diminished Value
There are three main types of diminished value:
- Inherent Diminished Value: The loss in value simply because the car has an accident history, regardless of repair quality.
- Immediate Diminished Value: The drop in value right after an accident, before any repairs are made.
- Repair-Related Diminished Value: The loss in value due to subpar repairs or visible damage.
What Is Depreciation?
Depreciation is the natural decline in your car’s value over time due to age, mileage, and wear and tear. Unlike diminished value, depreciation happens to every vehicle, regardless of whether it’s been in an accident.
Definition of Depreciation
Depreciation is the difference between your car’s original purchase price and its current market value. For example, a new car that costs 30,000 may be worth only 20,000 after three years due to depreciation.

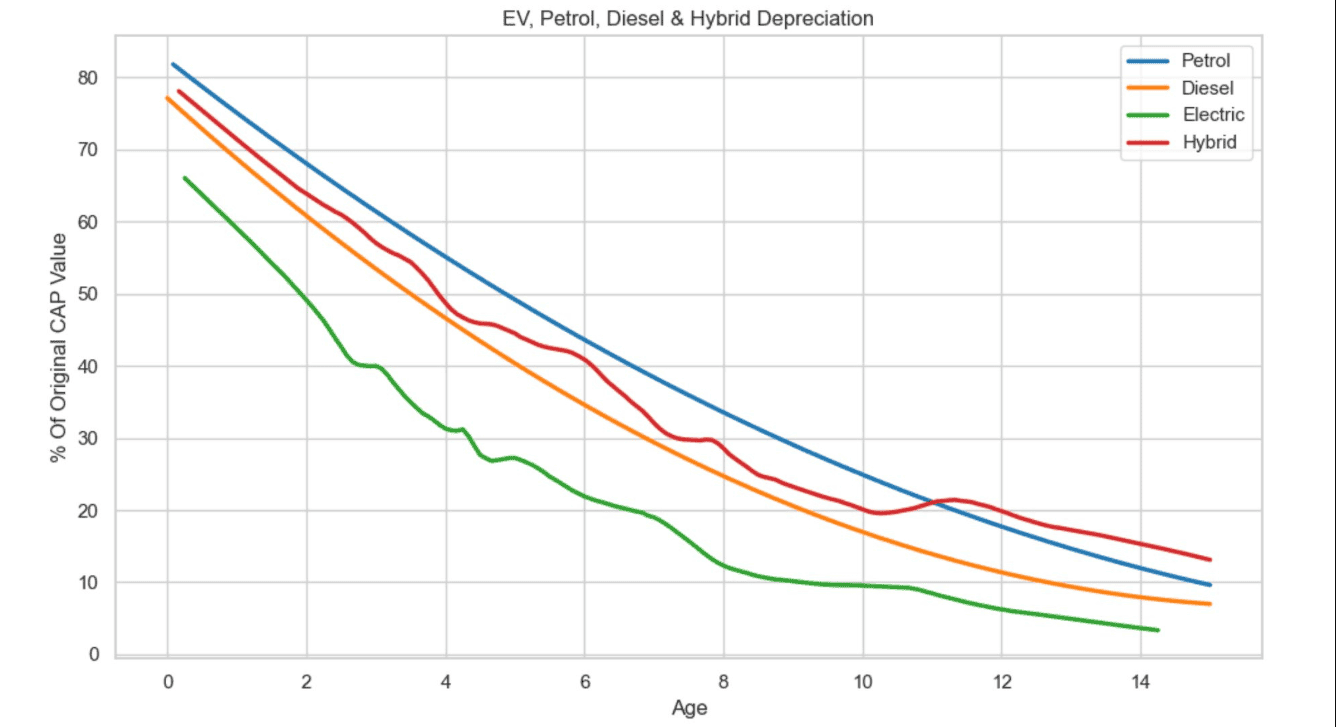
How Depreciation Works Over Time
Depreciation is most significant in the first few years of a car’s life. On average, a new car loses about 20-30% of its value in the first year and up to 50% within three years. After that, the rate of depreciation slows down.
Factors That Influence Depreciation
Several factors affect how quickly a car depreciates:
- Make and Model: Some brands and models hold their value better than others.
- Mileage: Higher mileage typically leads to faster depreciation.
- Condition: Regular maintenance and care can slow depreciation.
- Market Trends: Economic conditions and consumer preferences can impact resale value.
Key Differences Between Diminished Value and Depreciation
While both diminished value and depreciation reduce your car’s worth, they are caused by different factors and occur under different circumstances.
Timing: When Each Concept Applies
- Diminished Value: Applies after an accident or damage, even if the car is repaired.
- Depreciation: Occurs continuously over time, starting the moment you drive the car off the lot.
Causes: Accidents vs. Natural Wear and Tear
- Diminished Value: Caused by accidents, collisions, or other damage that affects the car’s history.
- Depreciation: Caused by age, mileage, and general wear and tear.
Financial Impact: How They Affect Resale Value
- Diminished Value: Can significantly reduce resale value, especially if the accident history is disclosed.
- Depreciation: Affects all cars but can be mitigated through proper maintenance and care.
Why Understanding These Differences Matters
Knowing the difference between diminished value and depreciation can help you make informed decisions as a car owner, buyer, or seller.
For Car Owners: Protecting Your Investment
Understanding diminished value can help you negotiate better insurance settlements after an accident. Knowing how depreciation works can help you maintain your car’s value over time.
For Insurance Claims: Maximizing Your Compensation
If your car has been in an accident, you may be entitled to compensation for diminished value. However, many insurance policies don’t automatically cover this, so you’ll need to advocate for it.
For Buyers: Evaluating a Used Car’s True Value
When buying a used car, it’s important to consider both depreciation and diminished value. A car with an accident history may have a lower price, but it could also come with hidden issues.
How to Calculate Diminished Value and Depreciation
Calculating these values can help you understand your car’s worth and negotiate better deals.

Methods for Calculating Diminished Value
- 17c Formula: A common method used by insurance companies, though it often undervalues the car.
- Appraisal: Hiring a professional appraiser can provide a more accurate estimate.
- Online Tools: Websites like Kelley Blue Book offer tools to estimate diminished value.
Tools and Formulas for Measuring Depreciation
- Straight-Line Depreciation: (Original Cost – Salvage Value) / Useful Life.
- Online Calculators: Tools like Edmunds or CARFAX can help estimate depreciation.
- Market Comparisons: Compare your car’s value to similar models on the market.
Tips for Minimizing Diminished Value and Depreciation
While you can’t completely avoid these issues, there are steps you can take to mitigate their impact.

Maintaining Your Vehicle’s Condition
- Keep up with regular maintenance.
- Address minor issues before they become major problems.
- Keep detailed service records.
Handling Accidents and Repairs Effectively
- Choose reputable repair shops.
- Use original manufacturer parts for repairs.
- Document all repairs and keep receipts.
Choosing the Right Insurance Coverage
- Look for policies that cover diminished value.
- Consider gap insurance to cover depreciation if your car is totaled.
Real-Life Examples of Diminished Value vs. Depreciation
Case Study 1: Post-Accident Diminished Value
John’s 2018 SUV was worth 25,000 before a rear−end collision. After 5,000 in repairs, its value dropped to 18,000 due to diminished value. John successfully filed a diminished value claim with his insurance company to recover 7,000.
Case Study 2: Long-Term Depreciation
Sarah bought a new sedan for 30,000. After Five Years And 60,000 miles,it’s now worth 12,000 due to depreciation. By maintaining the car well and keeping mileage low, she slowed the rate of depreciation.
FAQs About Diminished Value and Depreciation
Can You Recover Diminished Value After an Accident?
Yes, but you’ll need to file a claim with your insurance company or negotiate with the at-fault driver’s insurer.
Does Depreciation Affect New and Used Cars Differently?
Yes, new cars depreciate faster, while used cars have already experienced the steepest drop in value.
How Do Insurance Companies Handle Diminished Value Claims?
It varies by policy and state. Some insurers automatically include diminished value coverage, while others require you to request it.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between diminished value and depreciation is crucial for anyone who owns, buys, or sells cars. While depreciation is an inevitable part of car ownership, diminished value can be mitigated with the right knowledge and strategies.
By maintaining your vehicle, handling accidents effectively, and choosing the right insurance coverage, you can protect your investment and maximize your car’s value. Whether you’re filing an insurance claim or shopping for a used car, knowing these concepts will help you make smarter decisions.